What is a Cell Tower?
Cell towers, also known as cell sites, are where electric communications equipment and antennae are mounted, allowing the surrounding area to use wireless communication devices like telephones and radios.
Cell towers are usually built by a tower company or a wireless carrier when they expand their network coverage or capacity, providing a better reception signal in that area. Cell towers are basically everywhere across the United States, although some cities have more than others. And Millman Land was there since the late 1990s, ensuring that the cell towers are all properly inspected.
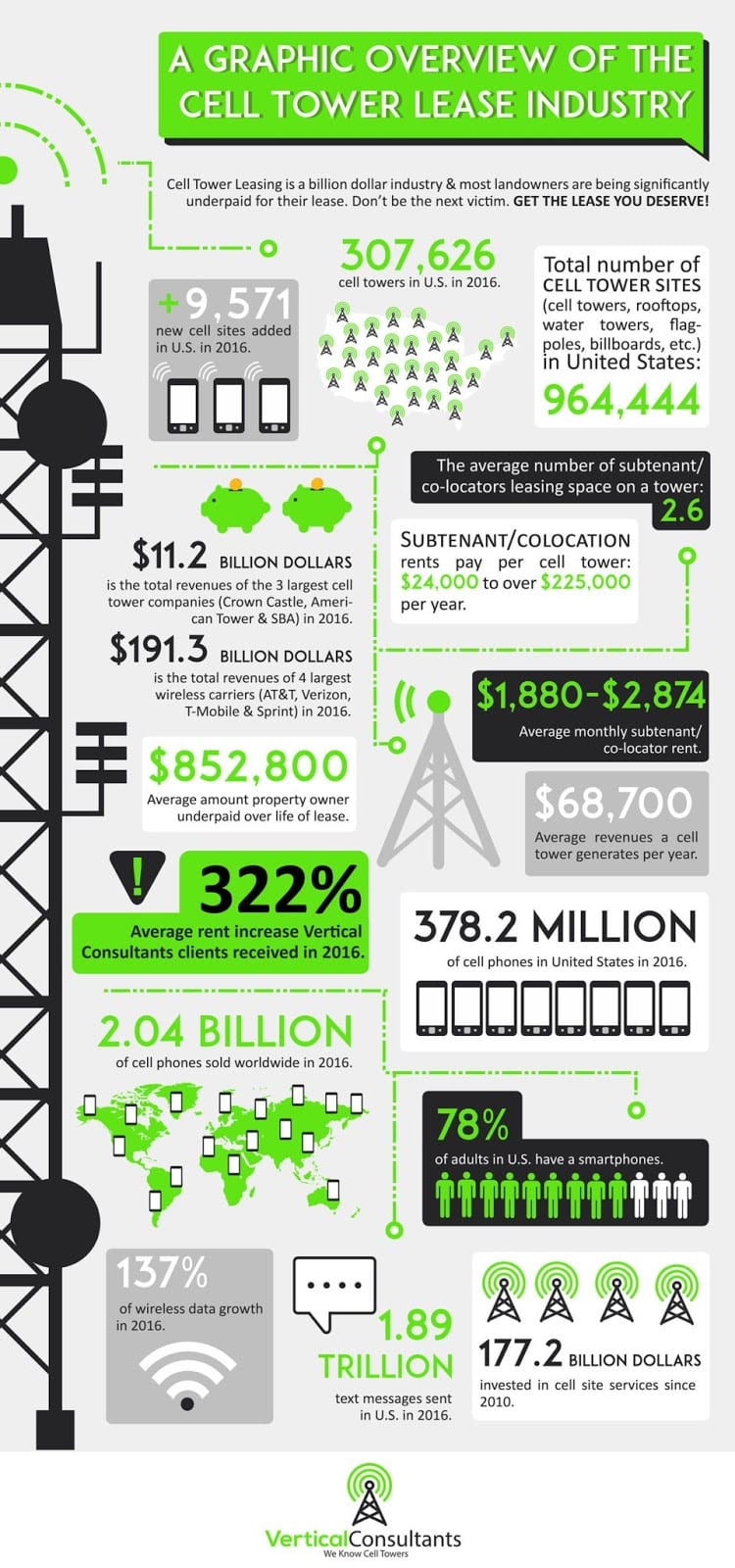
There are currently more than 307,000 cell towers in the United States. Sometimes they can be spotted on tops of buildings. Other times cities require cell towers to blend into the cityscape seamlessly. Rural areas sometimes hide them in treescapes, disguising them as a tree.
Our wireless services include cell tower surveys, cell tower audits and As-builts. In this article, we aim to tell you more about cell towers and how they work. We also want to address people’s growing concerns over 5G and put to rest the rumors.
How Do Cell Towers Work?
There are over 300 million cell phones being used daily in the United States. Whenever a cell phone is used, it emits an electromagnetic radio wave, called a radio frequency, that is received by the nearest cell tower’s antenna.
Once the cell tower receives this signal, it will transmit the signals to a switching center. This allows the call to be connected to either another mobile phone or to a telephone network. It’s crazy to think all of this happens in mere seconds.
Related: The Ultimate Guide to ALTA Surveys
Parts of a Cell Tower
The insanely fast technology of a cell tower is due to its parts. You’ll hear us mentioning cell carriers a lot in this section. That’s because a lot of the parts of a cell tower are provided by individual cell carriers, also known as wireless networks.
There are four wireless networks in the United States that have the best coverage. Right now the top provider is Verizon, which has 70% 4G coverage. AT&T is in close second with 68%. T-Mobile has 62% and Spring is in fourth with 27%, a major decline in coverage.
The Tower
There are actually four different types of cell towers. The first kind is known as a lattice tower. Also called a self-supporting tower, this type of tower offers incredible flexibility. It usually has three or four sides with similar shaped bases.
The second type of tower is a monopole tower. This type of tower features a single steel or concrete tube tower, usually under 50 meters. It only requires one foundation. The antennas are attached to the exterior.
A guyed tower is cost-effective but requires a bigger amount of land. It’s usually built 100 meters or greater, connected buy guy wires to anchor and support it. They are attached to the ground in all directions. Most radio and television towers are guyed towers.
The fourth type is the stealth tower, which we briefly touched upon before. Often required by councils, these are more expensive than the other three options but aim to beautify the community they’re in. They require additional materials that help them hide in plain sight. While much more appealing, they often do not provide the same amount of capacity for tenants.
The Equipment
The equipment on cell towers includes transceivers and other supporting technology. These are installed in cabinets or shelters or any other way that wireless carriers choose to protect them. Some even create outdoor cabinets on concrete pads or prefabricated equipment shelters.
The Antennas
Alright, we’ve touched on antennas a lot, but what are they? There are multiple antennas attached to a cell tower, typically mounted on a head frame. Some towers even have up to 15 antennas per carrier. This number really depends on the antenna’s performance, coverage and capacity requirements.
Utilities and Access
Carriers will also install utilities at the cell tower site. Each carrier has power to run to the site as well as phone service. Each cell tower also requires access by the carriers for initial installation and ongoing maintenance.
Related: Cell Tower Effectiveness Guide
Cell Tower Range
The aforementioned parts help determine just how far a cell tower can be a from a cell phone while still able to pick up its signal. That distance is determined by the connecting technology, landscape features (hills, trees and buildings), the power of the tower’s transmitter, the size of the cellphone network and the network’s design capacity.
What’s interesting is that a cell tower will sometimes have their transmitter seat to a lower power on purpose to ensure it doesn’t interfere with neighboring cells.
But even with all of those factors, the typical cell tower can provide service up to 45 miles away. That’s quite impressive! Let’s take a closer look at what various components affect a cell tower’s range and effectiveness.
What Affects a Cell Tower’s Range?
The range of a cell tower is not a fixed figure. That’s because there are so many variables when it comes to the range in which a cell tower connects a mobile device. The most common variables include:
- How hight the antenna is over the surrounding landscape.
- The frequency of the signal in use.
- The rated power of the transmitter.
- The directional characteristics of the antenna array on the site.
- Nearby buildings and vegetation absorbing and reflecting radio energy.
- The local geographical or regulatory factors and weather conditions.
Cell towers are often built in areas with high population densities. That’s because these cities have the most potential cell phone users. For that reason, you’ll often find cell towers “overlapping” in more crowded areas. This helps to avoid interference problems.
If you find yourself wondering why you don’t have a signal on your cell phone, it could be because you’re too far from a tower or because the cell phone signal has been decreased by hills, large buildings or other structures. You may also lose your signal if a lot of people are attempting to use the cell tower at the same time. That often leads to calls getting dropped.
While driving, your phone can switch from one cell tower to the next mid-conversation. As you continue your journey, the cell phone will pick the strongest signal and release the weaker cell tower, making it available to another caller.
Another factor that could affect your signal is a problem with the cell tower. With help from surveyors like Millman National Land Service, these issues can be identified so they don’t turn into a major headache.
What Are the Safety Standards for Cell Towers?
According to the Connecticut Department of Public Health, many standards are put in place to protect people around cell towers. For starters, the FCC sets strict limits on the amount of RF energy that cell antennas can give.
These limits factor in the potential unknowns regarding the effects of RF radiation on public health. In addition to these limits, cell towers are often restricted with fences and warning signs. That way, no one unintentionally comes into close contact with the transmitting antenna.
What Are Cells-On-Wheels?
When most people think of cell towers, they tend to picture permanent structures. However, that’s becoming a thing of the past thanks to cells-on-wheels (also humorously referred to as COWs). These portable structures can easily be towed into locations.
They are great for providing temporary cell service during a power outage. Or, if the equipment is damaged, it can be used until repairs have been made.
Is 5G Dangerous?
With the coronavirus pandemic continuing to strike fear into people all over the world, it’s no surprise that we’re seeing an abundance of conspiracy theories regarding COVID-19 and how it’s spread. One of the most bizarre are the Facebook posts claiming that 5G has created the coronavirus pandemic. While definitely a little on the radical side, there are still some health concerns about 5G that are a bit more grounded in science.
But no: 5G did not cause the coronavirus.
Related: A Complete Guide to Small Cells
What is 5G?
Big wireless carriers like AT&T, Verizon and Spring have started to implement 5G as the new wireless standard. In a year or so, 5G will be available throughout the United States. There are currently some devices that use 5G, like Samsung’s Galaxy S10, but most current phone models do not support 5G just yet.
5G will basically be a major improvement on network performance. It’s considered a huge upgrade from 4G, which debuted back in 2009. While 4G delivers 10 Mbps, 5G will deliver peak speeds between 10 and 20 Gbps. It’s also more ideal for video game streaming, downloading movies and other heavy-duty data activities since network latency will drop from 30ms to 1ms.
While this is all exciting technology-wise, there are currently growing concerns over the health risks of 5G, since it’s a stronger radiofrequency. While 5G has not caused the coronavirus, are there other dangers lurking on cell towers across the United States?
Interested in implementing 5G into your next cell tower project? Visit this page to learn how Millman National Land Services can help you.
How Dangerous Is Radiofrequency Radiation?
So what are these Facebook conspiracy theorists claiming about 5G? There are growing concerns that 5G’s higher energy radiation will bring potentially damaging effects to human beings near the cell towers. This increase in radiofrequency radiation will supposedly lead to cancer, premature aging and disruption in cell metabolism thanks to damage done to human DNA.
Is this true?
Well, not to be an alarmist, but RFR can also be found in your microwave, radios and other daily activities and common household items. Even computer monitors. Because of this, it’s already been determined that RFR is not really all that dangerous unless used in certain circumstances.
What are these dangerous circumstances? Well, the radiation has to be “ionizing” to be strong enough to break chemical bonds. This includes x-rays and gamma rays. Wi-fi and FM radio are “non-ionizing,” meaning they’re too weak to cause any damage. Non-ionizing RFR, like those found coming from cell towers, have no known mechanism that causes biological effects or DNA mutations. In other words, it’s completely safe.
The Risks of 5G
So 5G is a new technology – a stronger technology. Should people be concerned? Currently, 5G is a non-ionizing RFR, meaning it’s not able to do any real damage.
Many conspiracy theories point towards the fact that 5G will require more transmitters. Since there are more popping up in cities, towns and neighborhoods, will the dose be higher? While a reasonable question to ask, 5G cell towers are still not a threat, even when there’s more cropping up. The electromagnetic radiation you withstand by walking outside is far greater than a 5G cell tower.
But what about 5G’s higher gigahertz frequency? Since it’s higher, is it more dangerous to living organisms? Currently, there’s no science supporting this. The FCC has also stated that there are no health problems currently associated with cell towers.
“For 5G equipment, the signals from commercial wireless transmitters are typically far below the RF exposure limits at any location that is accessible to the public,” said Neil Derek Grace, a communications officer at the FCC.
While scientists are continuing to look into 5G technology and possible health risks, there is currently nothing to support that 5G cell towers do real harm to humans or animals.
The good news is that the FCC isn’t the only one who has declared 5G safe. According to this Forbes article, the World Health Organization and the FDA have proclaimed that this new technology poses no public health risk.
Related: Why Do Cell Phone Signals Go Bad? What You Need To Know
What Is the Future of Cell Towers?
According to statistics, there are likely nearly half a million mobile wireless cell sites found in the United States. Now, a large number of new investments will be going toward transitioning these sites into 5G.
However, it’s important to note that we likely won’t see as many unique cell sites in the future. Why? Because many providers now want to recombine towers. 4G and 5G technologies allow cell providers to do this.
And it significantly decreases their operating expenses since they don’t need to operate and maintain unnecessary towers. So instead of more cell sites in the future, we’re more likely to see fewer.
How Millman National Land Service Can Help With Your Cell Towers
Our company has been on the front lines in helping telecommunication providers transition into 5G. We provide services like co-location cell site surveys that allow two telecom providers to use the same tower.
What’s more, we’ll take care of all the surveys that go into creating a new cell tower. Want to learn more about our telecommunication services?
If you’re ready to get all your surveying needs taken care of, then contact us today, and we’ll get started on your next project.
Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, more and more cell towers will crop up around the United States. But as we await 5G technology, there are still over 307,000 cell towers around the nation that ensure we get cell phone service almost everywhere we go. It’s incredible what technology is behind these towers.
At Millman National Land Service, we ensure these cell towers are not only meeting health and safety standards, but are working as originally intended. Contact us today if you’re in need of cell tower surveys or audits.